© Drew Angerer/Getty Images It only takes a few moments to check your storage on a Windows computer. Drew Angerer/Getty Images
- Microsoft Storage Explorer Proxy
- Microsoft Storage Explorer Azure
- Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer Tutorial
- Microsoft Azure Explorer es una herramienta para ver los objetos que se encuentran en nuestras Storage Accounts de Azure para subir o descargar.
- Open Storage Explorer. In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the file share you wish to view. Expand the storage account's File Shares. Right-click the file share you wish to view, and - from the context menu - select Open.
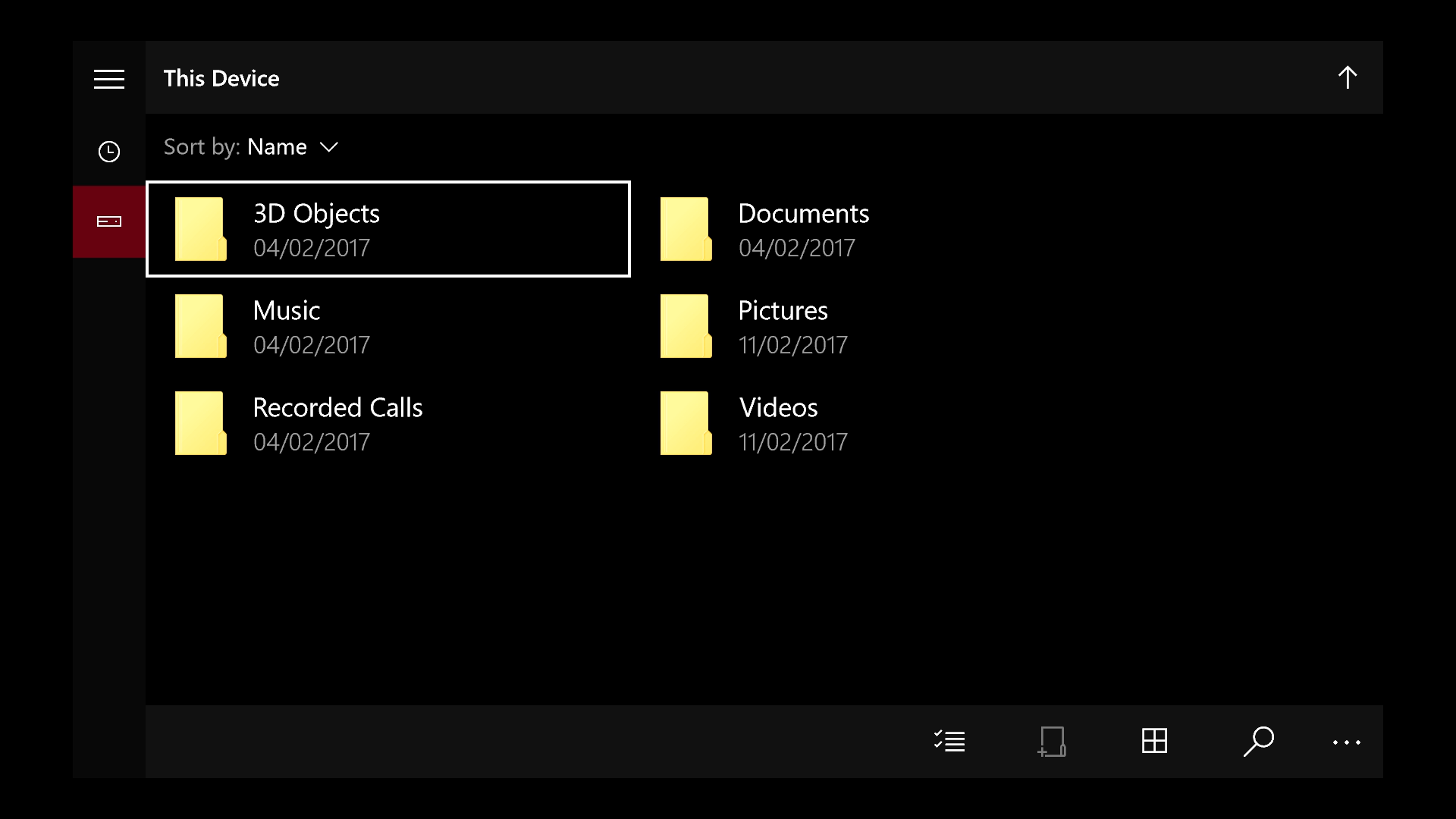
- You can check your Windows computer's storage space through the 'This PC' menu in your File Explorer.
- You can also open Windows' Settings app, which lets you see your available storage, as well as how your storage is currently being used.
- Visit Business Insider's Tech Reference library for more stories.
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer 1.6.2 free download from DriverPack Solution. Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer is a standalone app that makes it easy to work with Azure Storage data on Windows, macOS, and Linux. The app can connect to storage accounts hosted on Azure, national clouds, and Azure Stack. This guide summarizes solutions for issues that are commonly seen in Storage Explorer. Azure RBAC permissions issues. About Storage Explorer Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer is a standalone app that makes it easy to work with Azure Storage data on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
No matter what kind of Windows computer you have — a desktop, laptop, or tablet — it has at least one hard drive that stores your programs, settings, and data.
It doesn't matter whether that drive is a traditional spinning platter or a more modern solid-state drive (SSD); either way, Windows gives you two easy ways to check your storage, and you can use whichever method is more convenient for you.
Here's how to do both.
Check out the products mentioned in this article:
Windows 10 (From $139.99 at Best Buy)
Acer Chromebook 15 (From $179.99 at Walmart)
How to check your Windows storage space using File Explorer
This is a fast and easy way to see how much storage space you have left, and only takes a few clicks.
1. Open any folder to launch the File Explorer.
2. In the navigation pane on the left side of the folder, click 'This PC.' You can also simply type 'This PC' in the text box at the top of the folder.
3. You should see all your hard drives displayed, with the available storage space displayed under each drive.
© Dave Johnson/Business Insider When you choose 'This PC,' you can see a snapshot of your computer's storage usage. Dave Johnson/Business InsiderHow to check your Windows storage using Settings
This is an alternate way to see how much storage space Windows has. It has the advantage of providing additional information.
1. Click the Start button and then click the Settings icon, which looks like a gear.
2. Click 'System,' and then, in the pane on the left, click 'Storage.'
3. You should see details about your primary hard drive, called 'C:.' Here, Windows will show you the remaining storage space, as well as how your drive is currently being used. If you click any category, you'll see additional options for managing this storage space.
© Dave Johnson/Business Insider The Storage option in Settings shows you how your hard drive's storage space is being used. Dave Johnson/Business Insider4. To see the storage space remaining on any other drives on your PC, scroll down and click 'View storage usage on other drives.'
5. You can click other drives to see a similar breakdown by category.
© Dave Johnson/Business Insider Click a drive to see details about that drive and to take action to manage your storage, if needed. Dave Johnson/Business InsiderRelated coverage from Tech Reference:
-->Overview
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer is a standalone app that makes it easy to work with Azure Storage data on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
In this article, you'll learn several ways of connecting to and managing your Azure storage accounts.
Prerequisites
The following versions of Windows support Storage Explorer:
- Windows 10 (recommended)
- Windows 8
- Windows 7
For all versions of Windows, Storage Explorer requires .NET Framework 4.7.2 at a minimum.
The following versions of macOS support Storage Explorer:
- macOS 10.12 Sierra and later versions
Storage Explorer is available in the Snap Store for most common distributions of Linux. We recommend Snap Store for this installation. The Storage Explorer snap installs all of its dependencies and updates when new versions are published to the Snap Store.
For supported distributions, see the snapd installation page.
Storage Explorer requires the use of a password manager. You might have to connect to a password manager manually. You can connect Storage Explorer to your system's password manager by running the following command:
Storage Explorer is also available as a .tar.gz download. If you use the .tar.gz, you must install dependencies manually. The following distributions of Linux support .tar.gz installation:
- Ubuntu 20.04 x64
- Ubuntu 18.04 x64
- Ubuntu 16.04 x64
The .tar.gz installation might work on other distributions, but only these listed ones are officially supported.
For more help installing Storage Explorer on Linux, see Linux dependencies in the Azure Storage Explorer troubleshooting guide.
Download and install
To download and install Storage Explorer, see Azure Storage Explorer.
Connect to a storage account or service
Storage Explorer provides several ways to connect to Azure resources:
Sign in to Azure
Note
To fully access resources after you sign in, Storage Explorer requires both management (Azure Resource Manager) and data layer permissions. This means that you need Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) permissions to access your storage account, the containers in the account, and the data in the containers. If you have permissions only at the data layer, consider choosing the Sign in using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) option when attaching to a resource. For more information about the specific permissions Storage Explorer requires, see the Azure Storage Explorer troubleshooting guide.
In Storage Explorer, select View > Account Management or select the Manage Accounts button.
ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT now displays all the Azure accounts you're signed in to. To connect to another account, select Add an account...
The Connect to Azure Storage dialog opens. In the Select Resource panel, select Subscription.
In the Select Azure Environment panel, select an Azure environment to sign in to. You can sign in to global Azure, a national cloud or an Azure Stack instance. Then select Next.
Storage Explorer will open a webpage for you to sign in.
After you successfully sign in with an Azure account, the account and the Azure subscriptions associated with that account appear under ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT. Select the Azure subscriptions that you want to work with, and then select Apply.
EXPLORER displays the storage accounts associated with the selected Azure subscriptions.
Attach to an individual resource
Storage Explorer lets you connect to individual resources, such as an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container, using various authentication methods. Some authentication methods are only supported for certain resource types.
| Resource type | Azure AD | Account Name and Key | Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Public (anonymous) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage accounts | Yes | Yes | Yes (connection string or URL) | No |
| Blob containers | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| Gen2 containers | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| Gen2 directories | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| File shares | No | No | Yes (URL) | No |
| Queues | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | No |
| Tables | No | No | Yes (URL) | No |
Storage Explorer can also connect to a local storage emulator using the emulator's configured ports.
To connect to an individual resource, select the Connect button in the left-hand toolbar. Then follow the instructions for the resource type you want to connect to.

When a connection to a storage account is successfully added, a new tree node will appear under Local & Attached > Storage Accounts.
For other resource types, a new node is added under Local & Attached > Storage Accounts > (Attached Containers). The node will appear under a group node matching its type. For example, a new connection to an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container will appear under Blob Containers.
If Storage Explorer couldn't add your connection, or if you can't access your data after successfully adding the connection, see the Azure Storage Explorer troubleshooting guide.
The following sections describe the different authentication methods you can use to connect to individual resources.
Azure AD
Storage Explorer can use your Azure account to connect to the following resource types:

- Blob containers
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 containers
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 directories
- Queues
Azure AD is the preferred option if you have data layer access to your resource but no management layer access.
- Sign in to at least one Azure account using the steps described above.
- In the Select Resource panel of the Connect to Azure Storage dialog, select Blob container, ADLS Gen2 container, or Queue.
- Select Sign in using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and select Next.
- Select an Azure account and tenant. The account and tenant must have access to the Storage resource you want to attach to. Select Next.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the URL of the resource. Select Next.
- Review your connection information in the Summary panel. If the connection information is correct, select Connect.
Account name and key
Storage Explorer can connect to a storage account using the storage account's name and key.
You can find your account keys in the Azure portal. Open your storage account page and select Settings > Access keys.
- In the Select Resource panel of the Connect to Azure Storage dialog, select Storage account.
- Select Account name and key and select Next.
- Enter a display name for your connection, the name of the account, and one of the account keys. Select the appropriate Azure environment. Select Next.
- Review your connection information in the Summary panel. If the connection information is correct, select Connect.
Shared access signature (SAS) connection string
Storage Explorer can connect to a storage account using a connection string with a Shared Access Signature (SAS). A SAS connection string looks like this:
- In the Select Resource panel of the Connect to Azure Storage dialog, select Storage account.
- Select Shared access signature (SAS) and select Next.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the SAS connection string for the storage account. Select Next.
- Review your connection information in the Summary panel. If the connection information is correct, select Connect.
Shared access signature (SAS) URL

Storage Explorer can connect to the following resource types using a SAS URI:
- Blob container
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 container or directory
- File share
- Queue
- Table
A SAS URI looks like this:
- In the Select Resource panel of the Connect to Azure Storage dialog, select the resource you want to connect to.
- Select Shared access signature (SAS) and select Next.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the SAS URI for the resource. Select Next.
- Review your connection information in the Summary panel. If the connection information is correct, select Connect.
Local storage emulator
Storage Explorer can connect to an Azure Storage emulator. Currently, there are two supported emulators:
- Azure Storage Emulator (Windows only)
- Azurite (Windows, macOS, or Linux)
If your emulator is listening on the default ports, you can use the Local & Attached > Storage Accounts > Emulator - Default Ports node to access your emulator.
If you want to use a different name for your connection, or if your emulator isn't running on the default ports:
Start your emulator.
Important
Storage Explorer doesn't automatically start your emulator. You must start it manually.
In the Select Resource panel of the Connect to Azure Storage dialog, select Local storage emulator.
Enter a display name for your connection and the port number for each emulated service you want to use. If you don't want to use to a service, leave the corresponding port blank. Select Next.
Review your connection information in the Summary panel. If the connection information is correct, select Connect.
Connect to Azure Cosmos DB
Storage Explorer also supports connecting to Azure Cosmos DB resources.
Connect to an Azure Cosmos DB account by using a connection string
Instead of managing Azure Cosmos DB accounts through an Azure subscription, you can connect to Azure Cosmos DB by using a connection string. To connect, follow these steps:
Under EXPLORER, expand Local & Attached, right-click Cosmos DB Accounts, and select Connect to Azure Cosmos DB.
Select the Azure Cosmos DB API, enter your Connection String data, and then select OK to connect the Azure Cosmos DB account. For information about how to retrieve the connection string, see Manage an Azure Cosmos account.
Connect to Azure Data Lake Store by URI
You can access a resource that's not in your subscription. You need someone who has access to that resource to give you the resource URI. After you sign in, connect to Data Lake Store by using the URI. To connect, follow these steps:
Under EXPLORER, expand Local & Attached.
Right-click Data Lake Storage Gen1, and select Connect to Data Lake Storage Gen1.
Enter the URI, and then select OK. Your Data Lake Store appears under Data Lake Storage.
Microsoft Storage Explorer Proxy
This example uses Data Lake Storage Gen1. Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 is now available. For more information, see What is Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1.
Generate a shared access signature in Storage Explorer
Account level shared access signature
Right-click the storage account you want share, and then select Get Shared Access Signature.
In Shared Access Signature, specify the time frame and permissions you want for the account, and then select Create.
Copy either the Connection string or the raw Query string to your clipboard.
Service level shared access signature
You can get a shared access signature at the service level. For more information, see Get the SAS for a blob container.
Microsoft Storage Explorer Azure
Search for storage accounts
To find a storage resource, you can search in the EXPLORER pane.
As you enter text in the search box, Storage Explorer displays all resources that match the search value you've entered up to that point. This example shows a search for endpoints:
Note
To speed up your search, use Account Management to deselect any subscriptions that don't contain the item you're searching for. You can also right-click a node and select Search From Here to start searching from a specific node.
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer Tutorial
Next steps

