- Copay Coinsurance Deductible Out Of Pocket Expenses
- Explanation Of Deductible And Coinsurance
- Difference Between Copay Coinsurance Deductible And Out Of Pocket
- Copay Coinsurance Deductible Out Of Pocket 2019
- Out Of Pocket Vs Coinsurance
Deductibles can work differently depending on your health insurance plan. Generally, all payments you make for covered healthcare services will count toward your annual deductible, unless the payment is considered a copay. Copays are a fixed amount you pay to see your doctor or a specialist. Let’s say that your health insurance plan has a $1,000 deductible and 20 percent co-insurance and you use $10,000 in services. In this case, you will be required to pay the $1,000 plus 20 percent of the remaining $9,000, up to your total out-of-pocket maximum. Out-of-pocket; deductible does not apply Copays for certain specialty medications may be set to the amount of any available manufacturer-funded copay assistance. 20% coinsurance to max $250/prescription. $1,250 per plan year out-of-pocket; deductible does not apply Copays for certain specialty medications may be set to the amount of any available. 2 days ago In 2021, an HDHP is one with a deductible of $1,400 or more for an individual and $2,800 or more for a family, and an out-of-pocket maximum (the amount you must pay out of pocket for care, including the annual deductible) of $7,000 for an individual and $14,000 for a family. This amount includes money you spend on deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Once you reach your annual out-of-pocket maximum, your health plan will pay your covered medical and prescription costs for the rest of the year. Here’s an example. You have a plan with a $3,000 annual deductible and 20% coinsurance with a $6,350 out-of-pocket maximum.
You are here: SafePol>Health Insurance>FAQs>Deductible vs Coinsurance
Health Insurance, like any other type of insurance, has its own terminology. It is essential to understand it because, without it, a usefulhealth insurance comparisoncannot be made. Below we explain some of the most important health insurance terms so you can make a smart and educated decision when choosing a medical plan.
Premium

Premium is the amount you pay for insurance. Premiums are usually paid in monthly or quarterly installments.
Copayment

A copayment or copay is a fixed dollar amount you pay for covered medical services or when visiting a doctor. Copayments for primary care providers (PCPs) are usually lower than for visiting specialist doctors. They typically range between $5 – $50 for PCPs and $10 – $100 for specialists. HMO plans tend to have more health care services covered by copayments than PPO plans.
Deductible
A deductible is an amount you pay for eligible medical expenses before your insurance plan starts to pay. If your plan has copayments, for example, for doctors visits or prescription drugs, it is possible you’d pay only the copayment without paying off your deductible first.
Coinsurance
After you meet your deductible, you usually pay coinsurance. Coinsurance is health care costs sharing between you and your insurance company. The coinsurance typically ranges between 20% to 60%. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, it means you pay 20% for covered health care services, and your insurer pays the remaining 80%. The cost-sharing stops when medical expenses reach your out-of-pocket maximum.
Copay Coinsurance Deductible Out Of Pocket Expenses
Out-of-Pocket Maximum (OOPM)
Out-Of-Pocket Maximum or Out-of-Pocket Limit is the most you will have to pay for covered medical services in your plan year. When you reach it, your insurer will pay for all covered services. OOPM includes copayments, deductible, coinsurance paid for covered services. However, it doesn’t include insurance premiums.
OOPM = Copayments + Deductible + Coinsurance
Out-Of-Pocket Maximum in subsidized plans can be lowered by Cost-Sharing Reduction Subsidy.
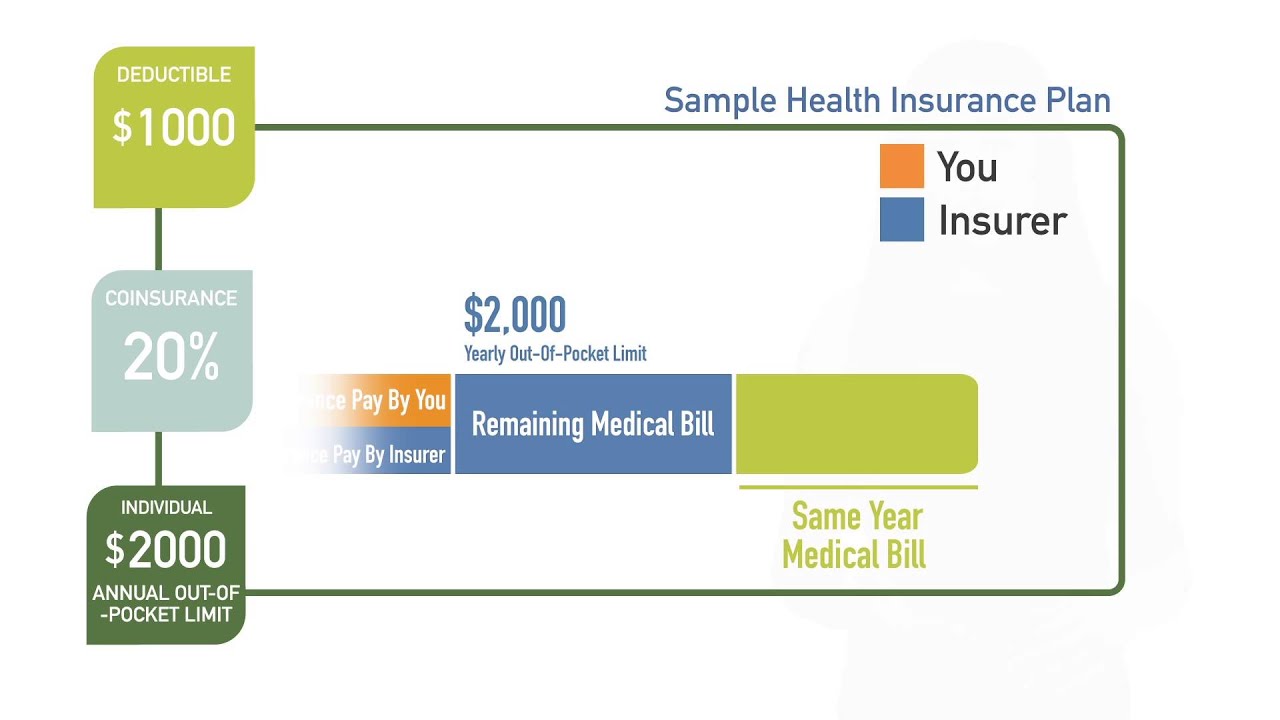
Example of how a typical health insurance plan works
Let’s say you have a health plan with:
- $20 copay for doctor visits
- $1,000 deductible
- 20% coinsurance
- $2,000 OOPM
Let’s say you go to see your doctor. You pay $20 copayment, and your OOPM drops to $1,920.
Explanation Of Deductible And Coinsurance
Next month you have surgery, which costs $15,000. First you pay $1,000 deductible, and your OOPM drops to $920 ( $1,920 – $1,000). The remaining balance to pay for the surgery is $14,000. You pay 20% coinsurance of $14,000, which is $2,800 and your insurance company pays 80% of $14,000, which is $11,200.

Now you will not have to pay the full $2,800 because your OOPM at this point dropped to $920. Therefore, you’ll pay the $920 and the rest $1,880 ($2,800 – $920) will also be paid by your health plan.

Difference Between Copay Coinsurance Deductible And Out Of Pocket
Let’s say after the surgery you need rehabilitation. The total cost for the rehabilitation visits and consultations is $2,000. You will pay nothing because you’ve already paid off your OOPM. Your health plan will pay the $2,000.
Copay Coinsurance Deductible Out Of Pocket 2019
The above example is just a simple illustration to give you a better understanding of how health plans may work. It assumes that all the medical services are rendered in the same plan year and are provided in your plan’s network. Out-of-network services may not be covered at all or would cost you much more.
Out Of Pocket Vs Coinsurance
In reality, your health insurance policy will have a different copayments, deductible, coinsurance, or OOPM. Switch 4k.
